
So it’s finally out, and boy is it big !! Well….actually….For Google(Somehow, still can’t bring myself to call it Alphabet. The word is so synonymous with the search engine since times immemorial), monetarily, it’s probably small. 2.42 Billion Euros is peanuts for the Internet behemoth. But what does matter to it is the impact this is going to enough on its products and services not just in the E.U., but throughout the world, which is why it is safe to bet that the company is going to all the way up to the E.C.J. if it has to. Fighting it out is already a forgone conclusion.
So, the following is my preliminary understanding of the Order. Please note though, that the complete text of the Order is not yet out, and so my preliminary opinion is based upon the Press Release, the Fact Sheet, and the Timeline of the case.:
1. The case concerns the display of products on a service called Google Shopping. Now since this service has not been rolled out in India till now, I have never personally had a chance to use it, but from what I have to come to understand (and do feel free to correct me if my understanding is wrong), the product “allows consumers to compare products and prices online and find deals from online retailers of all types, including online shops of manufacturers, platforms (such as Amazon and eBay), and other re-sellers.” (Update: Okay so I just realised that the words typed matter. They must indicate ones intent to purchase a product. So the service has been rolled out in India, but after some experimentation, the results appear to be limited.)

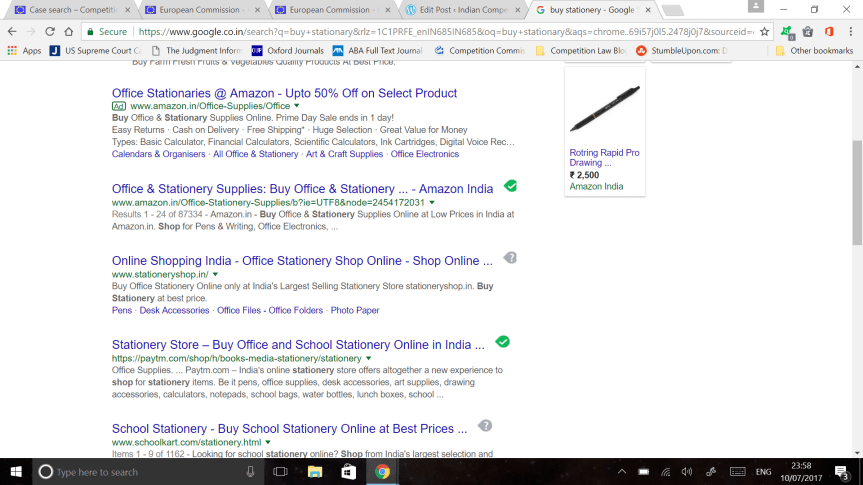
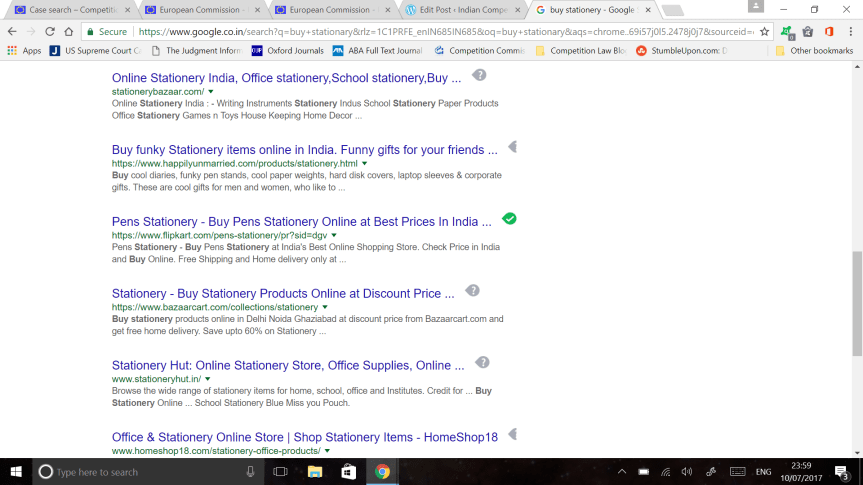
(Above: Google Shopping India: Personal experience on experimentation.)
2. From the above, the relevant market as per the Commission appears to be that of “shopping comparison websites/services”. The question to ask is, is there really such a definitive market in existence ?? Somehow, no matter which way one tries to describe it, it appears to be hard to cogently define it. After all, comparison of products can be done through the regular search, or they can be done through the individual websites, or they can be done through individual Applications (in the case of smartphones). Personally, I hardly used the Google results which appeared on the side. I (and perhaps many others) end up directly clicking on the “trusted/preferred” website (Amazon India, Flipkart, Ebay.in) and search directly for the product by jumping between these sites (not to mention to multiple options available on each individual website). It’s important to note that these website results do almost always come up among the top five to ten results on the first page, hence the lack of use of the Google Shopping. (See the pictures above as an example)
3. The fundamental premise of competition law, both in India as well as the E.U., is that any appreciable adverse affect on competition in the relevant market or abuse of dominance results in a harm to consumers. In the present case, however, was Google Shopping really so bad ?? Is there really an adverse affect on competition or an abuse of dominance ?? As already stated, the results which pop up under Google Shopping (which, it must be noted, are clearly differentiated), are merely the most relevant websites where you would find the product. And consumers do appear to be have A LOT of choice in the alleged relevant market. So even if the sponsored results do pop up on the side, does it really hurt anybody at all ?? In fact, from the Press Release, it appears that even the Commission is not sure if there is any actual detrimental affect on consumers, but rather only states “Google’s comparison shopping service [sic] make[s] significant gains in traffic at the expense of its rivals and to the detriment of European consumers.” A rather vague statement, but then, that may be because it is only a Press Release.
Google’s troubles in Europe are far from over. The Android Operating System and the Adsense cases are still pending, and the trend appears to be against the company. The three cases together could well become the triumvirate against what was once considered (and arguably still is), the most innovative company in the world.




